1.Low cost, returnable after six months
One robotic arm costs approximately 60,000-100,000 units, depending on the number of axes and brand—with multi-axis models boasting more flexible movement and well-known brands offering superior durability. While there's a significant initial investment, the total cost over time and months is equivalent to half a year's salary of a skilled stamping worker, and this does not include additional expenses such as social security contributions, welfare benefits, and overtime pay for human employees. In contrast, robotic arms only require routine maintenance, making them a cost-efficient alternative in the long run.
2.No payment, high efficiency and accuracy
Stamping robots operate without pay, offering extremely high efficiency and a much lower error rate compared to manual labor. Human workers are prone to fatigue after long hours of repetitive stamping tasks, which can lead to inconsistent product quality and even operational mistakes. Robots, however, maintain stable performance around the clock, which not only ensures uniform product standards but also reduces workers' reliance on manual skills. In China, the proportion of general laborers in the stamping industry is very high, and they are heavily reliant on years of accumulated manual techniques to handle complex stamping procedures. Society needs progress, and manufacturing must continue to be scientific and efficient. Stamping robots replacing manual labor will reduce workers' dependence on manual skills, freeing human resources to engage in more creative and value-added work such as equipment debugging and quality inspection.
3.Can replace dangerous manual operations
In some stamping fields, many processes are extremely dangerous. The stamping industry relies on the immense pressure and weight of the press for production, making manual operation very risky—even a split-second distraction can result in severe hand or arm injuries. Using stamping robots can alleviate business owners' concerns about workplace accidents and potential legal liabilities. Otherwise, compensation costs for work-related injuries could reach 300,000-400,000 yuan per incident, not to mention the negative impact on the company’s reputation and employee morale.
Long working hours: Robots can operate continuously 24 hours a day, with only necessary rest periods for regular maintenance and part replacement, which usually takes no more than a few hours per month. This uninterrupted operational capacity directly translates to higher production output, enabling factories to meet tight delivery deadlines and gain a competitive edge in the market.
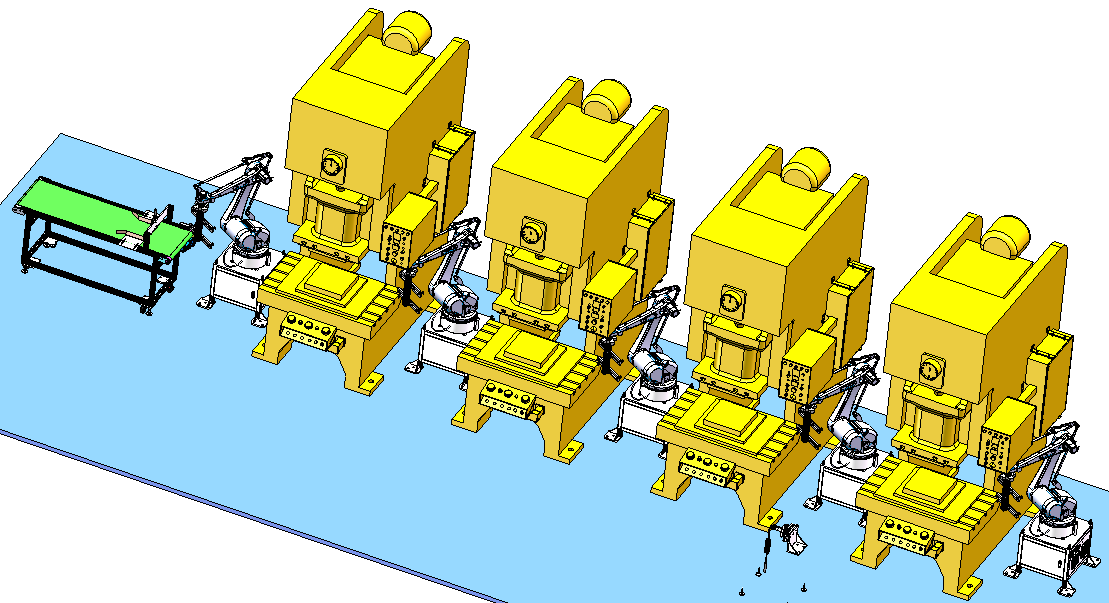
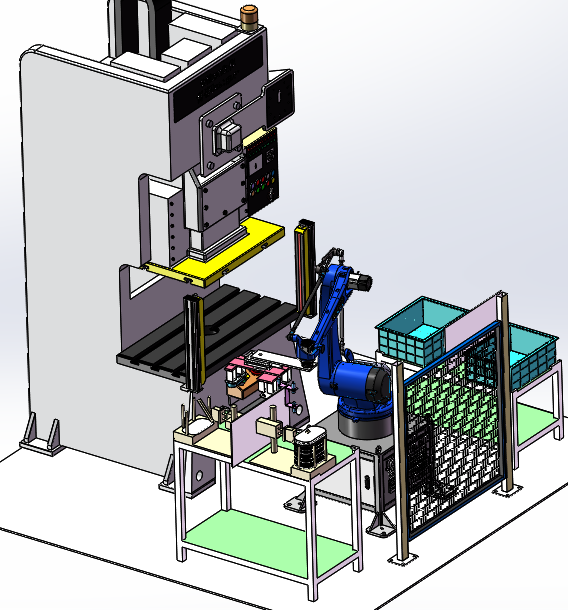
Stamping robots are primarily used for products that are unsuitable for progressive dies, such as irregularly shaped components that require precise positioning during the stamping process. After stamping, the product can be directly removed from the lower die, with the pick-up depth not exceeding 35mm and fully customizable according to the size of the workpiece. Different materials can be used for sheet metal stamping, including steel, aluminum alloy, and copper, expanding their applicability across diverse industries. It can operate as a standalone machine for small-scale production or online (asynchronously) for large-scale assembly line operations.
1.Safety: Whether operating as a standalone machine or in a multi-line system, the operator's hands remain in a safe area outside the working range of the die and press, reducing the risk of accidents to almost zero. Advanced safety sensors are also equipped on the robots, which can automatically stop operation if any foreign object enters the working zone, further enhancing workplace safety.
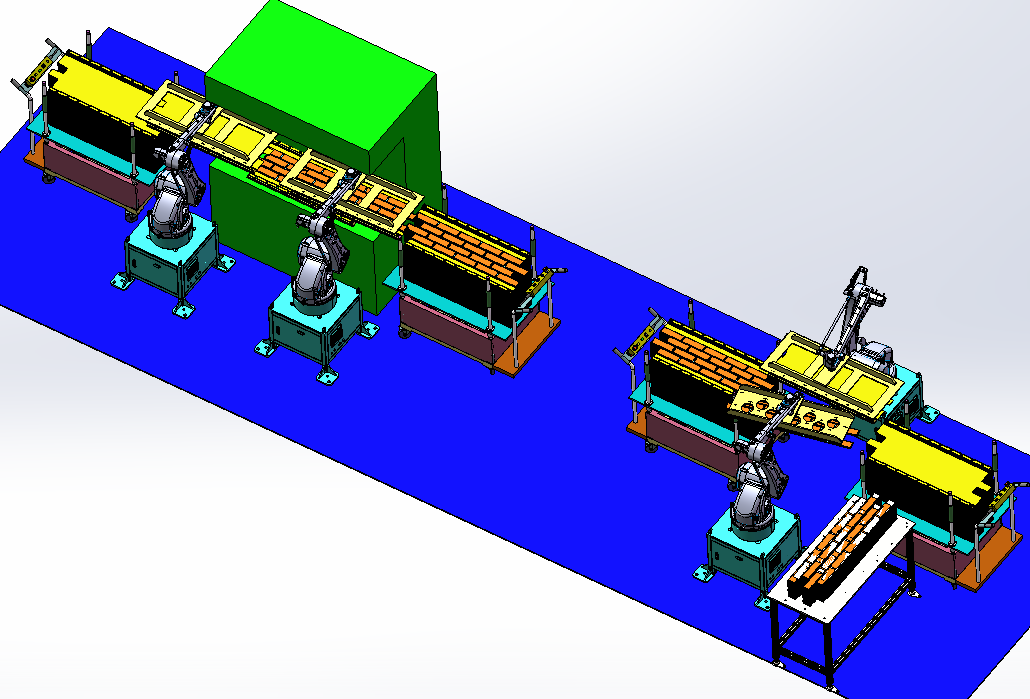
2.High Efficiency: Particularly noteworthy is the ability for two or more stamping robots to be connected online, forming a fully automated stamping line. Theoretically, the number of online machines is unlimited, with a production capacity of 600-900 PCS per hour, which is 2-3 times higher than manual production lines. Automatic feeding devices, when paired with stamping robots, further enhance efficiency by ensuring a continuous and stable supply of raw materials, eliminating the need for manual material handling.
3.Cost-Effectiveness: This is a general advantage that sets stamping robots apart from traditional production methods. Stamping robots are not limited in number, are easy to debug and switch—only the area fixture needs to be changed when changing the die, which can be completed within 30 minutes. This flexibility makes them ideal for small batches and customized production, making them highly cost-effective. Due to asynchronous operation, for multi-station multi-line operation, even if one process needs to stop for maintenance or die replacement, it will not affect the previous process, and subsequent processing machines can switch dies at any time without causing a complete shutdown of the entire production line, minimizing production downtime.
4.Convenience and Efficiency: Stamping robots of varying tonnage can be installed online to match different types of presses. When fixedly installed, they can operate independently for single-process stamping or in series for multi-process production, adapting to different factory layouts and production requirements. The number of adjacent robots connected is unlimited, allowing factories to expand their production capacity gradually as demand grows. Operation is also user-friendly: simply adjust the control panel mode button to switch between different working states, and turn off the power and air supply when the robotic arm is not in use, reducing energy consumption during idle periods.
Stamping robots have long working hours, capable of continuous operation 24 hours a day, while humans require rest periods, breaks, and vacation time, leading to inevitable production interruptions. Stamping robots can replace humans in hazardous operations, which is one of their most critical advantages in the stamping industry. In some stamping fields, such as heavy-duty metal stamping and high-speed precision stamping, many processes are highly dangerous. The principle of the stamping industry is to use the weight and pressure of a punch press for production, and human operation is very risky even with strict safety measures. The operation of a four-axis stamping robot eliminates this concern for employers; its precise movement and stable performance can handle the most dangerous stamping tasks with ease. Otherwise, the compensation costs for severed limbs and other serious injuries would be substantial, and the psychological impact on other employees could also disrupt the normal production order of the factory. In conclusion, stamping robots are an indispensable core equipment for the intelligent transformation of modern manufacturing.
If you are interested in stamping robots, please feel free to contact SZGHTECH for more information and application examples.


