Working Principle of CNC Lathe and Milling Machine Controller
Whether it is a CNC lathe controller or a CNC milling machine controller, its basic working principle is roughly the same. The controller controls the machine tool to perform various processing tasks by parsing the CNC programming instructions. Specifically, its workflow is as follows:
CNC programming and input: The operator or designer writes the CNC program through computer software, converts the design drawings or CAD models into standard G code and M code, and then inputs them into the CNC controller.
Motion instruction parsing: The CNC controller converts the received CNC instructions such as G code and M code into corresponding motion control signals. According to the processing requirements in the program, the controller calculates the moving path, speed and processing depth of each motion axis (X, Y, Z axis, etc.).
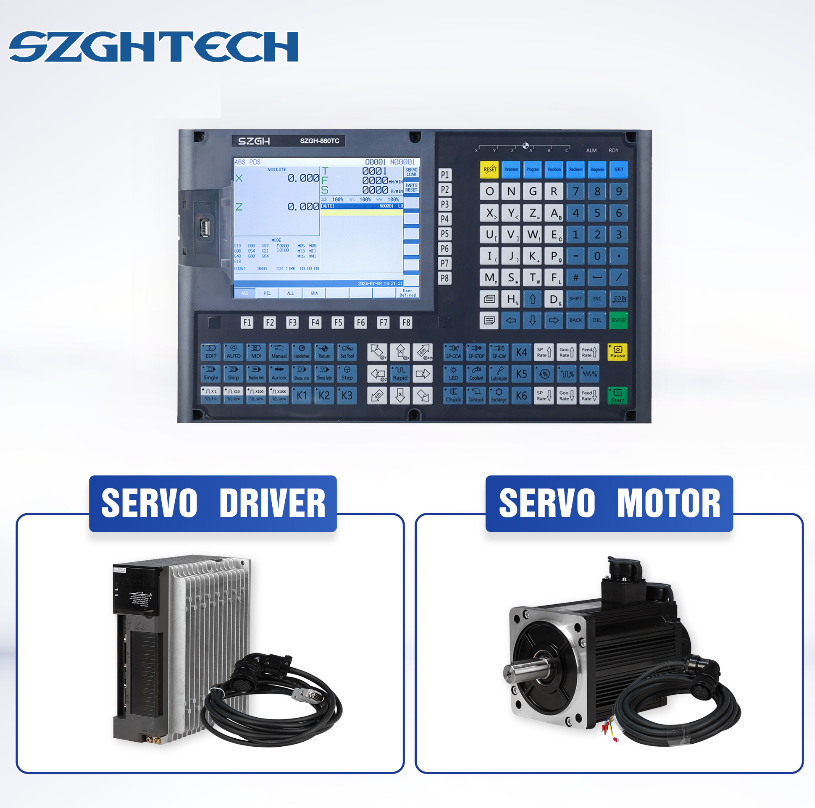
Controlling motion execution: The CNC controller controls the motor of the machine tool (such as servo motor, stepper motor, etc.) to drive each motion axis to achieve precise movement of the tool and workpiece. The lathe controller focuses on controlling the rotation of the workpiece and the feed motion of the tool, while the milling machine controller involves more complex control of the axial direction and tool angle.
Real-time feedback and adjustment: The CNC controller monitors the status of machine tool movement in real time, such as position, speed, load, etc. Through a closed-loop control system, the controller adjusts the motion trajectory based on sensor feedback information to ensure processing accuracy and stability.
Processing completion: Throughout the entire processing process, the CNC controller continuously manages the relative position of the tool and the workpiece to ensure that each processing step is accurate until the final product is completed.